Mall Maverick GA4 Series: Major Differences Between UA and GA4
There are many new and exciting changes with the introduction of Google Analytics 4 (GA4). Since GA4 is a completely new platform, it comes with various new features that Universal Analytics doesn’t have.
In this article we’re going to break down the main differences between the two platforms to give you a clear understanding of Google Analytics 4. This will help you to prepare for the migration and be able to compare your Shopping Center Website Universal Analytics reports with your GA4 reports.
Reporting Dashboard
The first change you are likely to notice in GA4 is the entirely new dashboard. It is more streamlined, and many of the reports you are used to with Universal Analytics are gone or have been moved.
Click here to understand the basics of GA4 reports and see examples of data collected.
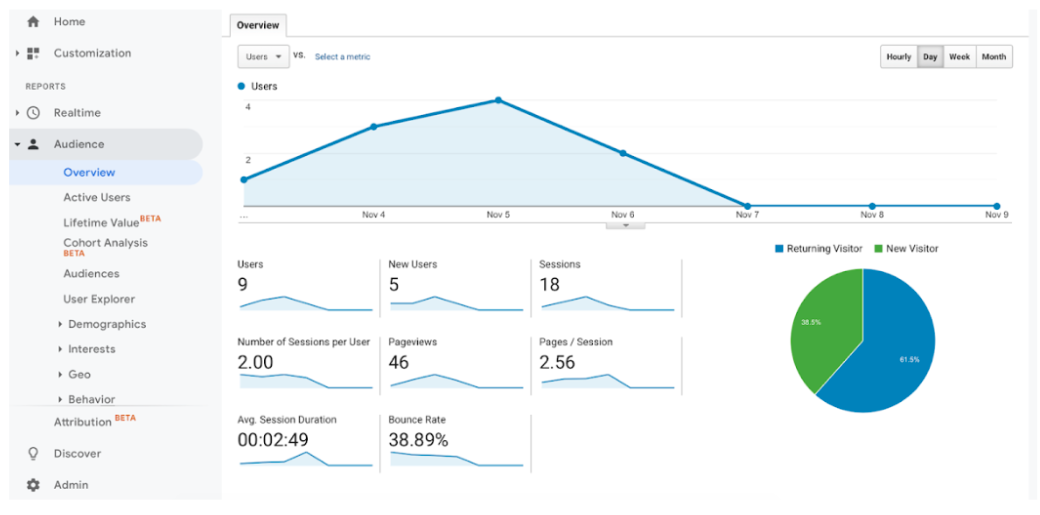
In Universal Analytics a navigation bar lists five categories of standard reports: real-time reports, audience reports, acquisition reports, behavior reports and conversion reports.
Measurement Model
The biggest difference between Universal Analytics and GA4 is the measurement model they use. Google Analytics 4 tracks data in a different way compared to Universal Analytics, mainly by using events and parameters instead of sessions. The metrics you’re used to seeing in UA, such as page views, users etc, will now fire as events on GA4
What’s important is that every activity taken by a user will be counted as an ‘event’ in GA4. This means that you will end up with much more detail on how users are engaging with your Shopping Center website.
Due to the different measurement model of GA4, some of the metrics may appear differently when comparing with UA and many of the familiar reports from Universal Analytics are not available.
Four types of events in GA4:
Automatically Collection Events - Are automatically triggered and logged on certain user activities. Click here to view the automatically collected events.
Enhanced measurement events - Also automatically triggered and logged on certain pre-defined user activities but are only logged when you enable “enhanced measurement” on the GA4 dashboard
Recommended Events - Events recommended by Google. These do not automatically get triggered and logged unless you manually implement them. To get this to work you must use the exact same event name and parameters supplied by Google.
Custom Events - Events you can create and use, which Google Analytics does not collect automatically. For example, menu link clicks on your Retail Center website.
Users
In Universal Analytics, there are two User metrics: Total Users, and New Users.
With Google Analytics 4, there are now three User metrics: Total Users, Active Users, and New Users.
Active Users
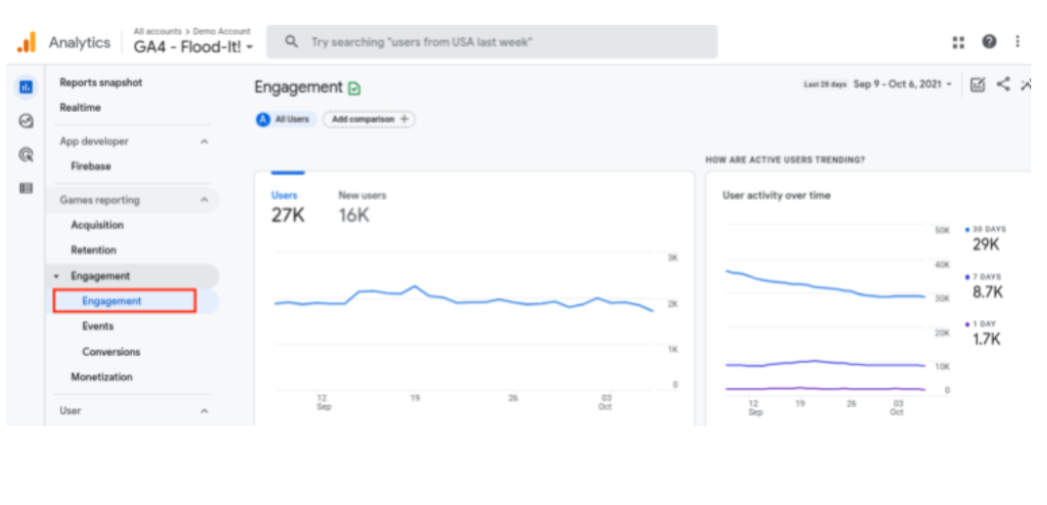
Active users take center stage in Google Analytics 4, and is one of the major changes from Universal Analytics. Active users are users who have engaged on your site over a certain time period. Google Analytics 4 looks at active users in terms of one day, seven days, and 30 days.
The reports in the GA4 engagement section allow users to look at audiences, events, monetization, and users. To get there, just sign in to your property and then click “Reports” > “Engagement.” You can then go to your engagement overview by clicking “Engagement” from the drop-down menu.
Total Users
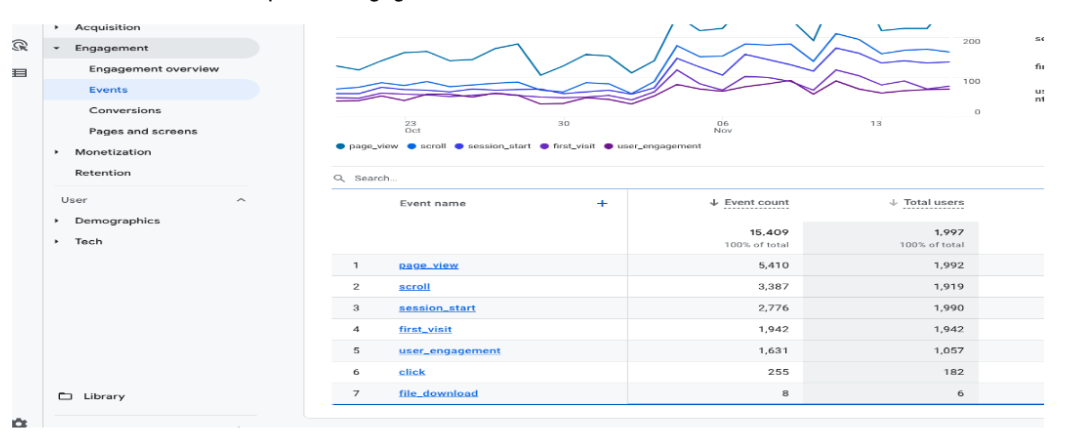
The total number of users as identified by their unique identifier e.g. cookie, user_id etc. that visited your Shopping Mall website during the time frame that you are looking at in your GA4 reports.
This can be found from Reports > Engagement > Events under the Total users column Total Users
New Users
Users who have visited your website for the first time.
This can be found from Reports > Engagement > Events beside the “first_visit” row
User measurements comparison (UA vs GA4)
Universal Analytics highlights Total Users (shown as Users) in most reports, whereas GA4 focuses on Active Users (also shown as Users). So, while the term Users appears the same, the calculation for this metric is different between UA and GA4 since UA is using Total Users and GA4 is using Active Users, which could result in different reports when comparing your UA analytics with GA4.
Sessions
In Universal Analytics, a session is a group of hits recorded for a user in a given time period. Whereas in GA4, a session is a group of events recorded for a user in a given time period.
Both UA and GA4 define a user as an individual who performs actions on your website in one or more sessions. Unlike in UA, the user activity is detected automatically in GA4. This may lead to higher active user counts in GA4.
Page Views
In general, Page Views should be fairly close between UA and GA4, generally within a few percentage points, since the Google tag fires on each page and generates a pageview. However, the differences can vary based on any filters you may have set up in Universal Analytics or Google Analytics 4. One thing to note is that Unique Pageviews are no longer a metric on GA4 but rather only the total number of views.
Pageview measurements comparison (UA vs GA4)
Author: Ardalan Amiri
Biography: Ardalan is the Operations Lead/Project Manager at Mall Maverick. He has his bachelor’s in Information Technology and has worked in the technology industry for over 10 years. He has extensive knowledge of digital marketing in the Retail Industry and has helped in delivering the successful launch of over 200 Shopping Center Websites and Directory Boards. This includes Web Development, Google Analytics, SEO and training clients on becoming experts with the Mall Maverick dashboard.